 If you’ve recently been diagnosed with high blood pressure, also known as hypertension<, chances are your healthcare provider has prescribed medication to help get it under control. Starting a new medication always raises questions and even some apprehension.
If you’ve recently been diagnosed with high blood pressure, also known as hypertension<, chances are your healthcare provider has prescribed medication to help get it under control. Starting a new medication always raises questions and even some apprehension.
Read to learn what you can expect when you start on your journey of blood pressure management with medication.
Understanding Your Blood Pressure Reading
When your blood pressure is taken, you get two numbers representing systolic and diastolic pressure. Systolic represents the pressure during your heartbeat. Diastolic is the pressure when the heart pauses between beats.
Normal blood pressure levels are considered to be under 120/80 mmHg. If your systolic or top number is 130 or more or your diastolic or bottom number is 80 or above, your doctor will likely prescribe medication.
Why Medication is Often Needed
Many lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and stress management, can promote a reduction in blood pressure.
However, when blood pressure reaches an unhealthy range, medication gives the quickest reduction in numbers to prevent damage to your arteries, heart, brain, and kidneys.
Medication makes life easier on your heart when pumping blood and helps prevent the hardening of the arteries.
Types of Blood Pressure Medications
There are several categories of blood pressure medications, each working in a different way.
- Diuretics remove excess fluid and sodium through increased urination.
- ACE inhibitors prevent blood vessels from narrowing so blood flows more easily.
- ARBs block angiotensin, a chemical that leads to a narrowing of blood vessels.
- Beta blockers slow your heart rate and force of contraction.
- Calcium channel blockers relax and widen blood vessels.
- Alpha blockers reduce nerve impulses to blood vessels, allowing them to relax.
- Vasodilators directly open up blood vessels to improve flow.
Your provider will prescribe the medication that’s most appropriate for your health profile and symptoms. Often, a combination of medications is used for the best effect.
Starting Your Medication
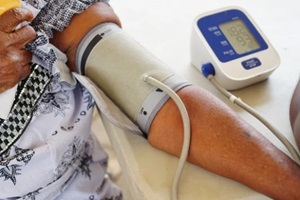 When first prescribed, you’ll typically start with a low dose taken once a day, often in the morning, to allow your system to adjust to the new drugs.
When first prescribed, you’ll typically start with a low dose taken once a day, often in the morning, to allow your system to adjust to the new drugs.
Over time, your dosage might be increased if necessary. Keep in mind that taking your meds at the same time daily helps keep your blood levels constant.
Some common tips when starting blood pressure medication:
- Take it with water and food if it causes an upset stomach.
- Sit or stand slowly to avoid dizziness.
- Avoid alcohol, as it can amplify effects.
- Write down when you take it to remember your schedule.
Monitoring Your Blood Pressure
One of the most essential things you can do when you start taking blood pressure medication is to monitor your numbers at home.
This helps you and your provider determine if your medication regimen is working or needs adjustment.
Get an easy-to-use home blood pressure monitor and check it a few times per week. Always take measurements at the same time each day and write them down.
Make a note of any dizziness, headaches, or other side effects, and report your readings to your healthcare provider.
Watching for Side Effects
When beginning a new blood pressure drug, be aware of potential side effects such as dizziness, fatigue, headache, nausea, diarrhea, elevated heart rate, and leg cramps.
Side effects tend to be relatively mild and often disappear within a few weeks as your body adjusts. Notify your provider if they are severe or don’t go away.
Avoiding Medication Interactions
To prevent complications, alert your healthcare provider about any other medicines or supplements you take, even over-the-counter products.
Certain pain relievers, antidepressants, herbal supplements, and even caffeine can interact with blood pressure drugs. Your pharmacist can also screen for interactions.
In addition, grapefruit can amplify the effects of some calcium channel blockers and statins, so check with your pharmacist. Limit alcohol, which can cause blood pressure to spike temporarily.
Meeting Treatment Goals
It may take a few weeks to a few months for your blood pressure medication to have its full effect. Be patient, take it faithfully as directed, and don’t stop abruptly.
Your provider will monitor your readings at follow-up visits and adjust your prescription as needed until treatment goals are met.
Once your blood pressure stabilizes, you’ll still need to take medication daily to maintain control.
High blood pressure doesn’t display obvious symptoms but silently damages arteries, the heart, and the kidneys. Medication prevents this threat to your health.
Incorporating Lifestyle Changes
 While your medication regimen is being established, you can amplify its effects by simultaneously focusing on lifestyle changes.
While your medication regimen is being established, you can amplify its effects by simultaneously focusing on lifestyle changes.
Losing extra weight, exercising more, reducing sodium and alcohol intake, managing stress, and quitting smoking can all assist in reducing your blood pressure numbers.
Your provider may be able to decrease your medication dosage if you are successful with lifestyle improvements.
But never alter or stop taking your medication without medical guidance. Lifestyle changes complement medication treatment but don’t replace it.
Work with Imperial Center Family Medicine for Effective Blood Pressure Management
Managing your blood pressure is a continuous process, and you have to be patient and persevere.
With the right medication plan and dedicated partnership with your healthcare providers, you’ll succeed in reducing your risks and improving your long-term health.
Imperial Center Family Medicine specializes in complete cardiovascular health, including blood pressure management.
Our experienced team stays on top of the latest treatment options and takes time to understand your unique health needs.
We’ll partner with you to create a personalized medication and lifestyle plan to get your blood pressure under control and keep it there. Contact us today at 919-873-4437 or online to take charge of your heart health.
